Examining the Influencing Factors of Students' Decision-making in the New College Entrance Examination: Based on the Sample from Guangdong
-
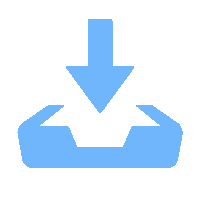
摘要: 新高考方案赋予学生选择考试性科目的权利,同时也对他们的选择力提出了要求。通过对第三批新高考试点省份之一的广东省部分高一学生进行抽样调查发现,决定学生选择科目的首要因素是重要他人的意见——包括家人、亲朋和教师等;其次是机会因素,包括未来职业和专业的需要等;最后则是体现自身优势和兴趣等的个人因素。可见,学生选科过程中受他人影响较大,自主选择能力不足。基于此,提高学生科目选择能力成为当务之急。建议建立系统的选科指导体系:学校需要打造选科指导课程体系,提升学生整体选择力;政府需要构建学生选科服务体系,提升教师和家长等重要他人的指导力。Abstract: Although the New College Entrance Examination expands students' right to choose, it also puts forward requirements to their choices. This article is based on a sampling survey of senior grade one students in Guangdong Province, one of the third batch of the pilot provinces that adopted the New College Entrance Examination, is aimed to discover those factors that affect students' choice of subjects. Based on theories of career decision and analysis of the data, it is found that the primary factor that determines the student's choice of subjects is the opinions of significant others, including family members, relatives, friends, and teachers. The second is the opportunity factor, including future career and professional needs, etc. The last is the personal factors that reflect one's own advantages and interests. Therefore, it can be concluded that students, to a large extent, are unable to choose independently, so improving students' ability to choose independently has become a top priority. Since students and parents urgently need more guidance and services, it is necessary to establish a systematic guidance system of subject selection. For schools, it is necessary to build a system of curriculum guidance for subject selection in order to enhance students' overall ability of making choices. For the government, it is necessary to set up a service system of subject selection to improve the guidance of significant others such as teachers and parents.
-
表 1 调查样本数据信息
样本类型 人数 比例 性别 男 791 42.32% 女 1078 57.68% 学校区域 珠三角 599 32.05% 粤东 235 12.57% 粤西 750 40.13% 粤北 166 8.88% 其他 119 6.37% 学校类型 省属 234 12.52% 市属 736 39.38% 区属 714 38.2% 镇属 138 7.38% 其他 47 2.51% 表 2 学生选科影响因素旋转成分矩阵
排序 影响因素 项目 负荷 贡献率(%) 累计贡献率(%) 1 重要他人 家人建议 .862 25.643 25.643 亲朋建议 .851 老师建议 .841 学校建议 .633 2 机会因素 拟报考专业的要求 .874 22.729 48.372 对应的专业选择范围 .871 未来职业选择需要 .856 3 科目因素 科目难易 .789 20.979 69.351 科目优势 .750 科目竞争 .726 科目兴趣 .594 表 3 学校类型的单因素方差分析统计量
因变量 方差来源 平方和 均方 F 显著性P 家人建议 组间 5.894 1.474 2.565 .037 组内 1070.688 .574 总数 1076.582 -
[1] 冯岩松. SPSS22.0统计分析应用教程[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社. 2015. [2] 华桦. 新高考下家长参与"大学准备"的影响因素: 家庭背景与学校支持[J]. 教育发展研究, 2019(12): 53-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHGJ201912011.htm [3] 张雨强, 顾慧, 张中宁. 普通高中生高考选考科目现状及影响因素研究——以浙江省5所高中首批选考学生为例[J]. 教育学报, 2018(4): 29-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XKJY201804005.htm [4] 刘宝剑. 关于高中生选择高考科目的调查与思考——以浙江省2014级学生为例[J]. 教育研究, 2015(10): 142-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYYJ201510019.htm -





 下载:
下载: